NEC develops compact millimeter-wave distributed antenna for Beyond 5G/6G
NEC Corporation has successfully
developed and demonstrated a radio-over-fiber system with a 1-bit fiber
transmission method making it possible to affordably build stable
millimeter-wave communication networks for Beyond 5G/6G. By utilizing this
method, high-frequency analog signals can be transmitted using an inexpensive
electrical-to-optical converter for general-purpose digital communications,
thereby enabling the realization of a compact distributed antenna unit at low
cost.
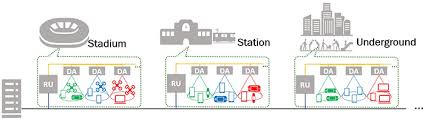
As a result, a stable millimeter-wave
communication environment can be inexpensively achieved in high-rise buildings,
underground malls, factories, railways, indoor facilities, and other
obstacle-laden environments.
NEC will be presenting its results at the IEEE
MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS2024) starting on June 16 (local
time) in Washington, D.C.
Development background
High-speed wireless communications leveraging
millimeter-wave technology are expected to be a key technology for Beyond
5G/6G. In particular, since approximately 80% of mobile communication traffic
occurs indoors, millimeter-wave is being considered as an indoor solution.
However, since there is significant propagation
loss and high linearity in the millimeter-wave frequency band, it is imperative
to ensure line of sight between base stations and terminals to achieve
sufficient quality of service (QoS). While dense installation of distributed
antenna units (DA) for direct transmission and reception of data with terminals
and avoiding obstacles is known to be effective in resolving these issues, the
size, power consumption, and cost of installing the required number of DA have
proven to be major issues.





























Leave A Comment